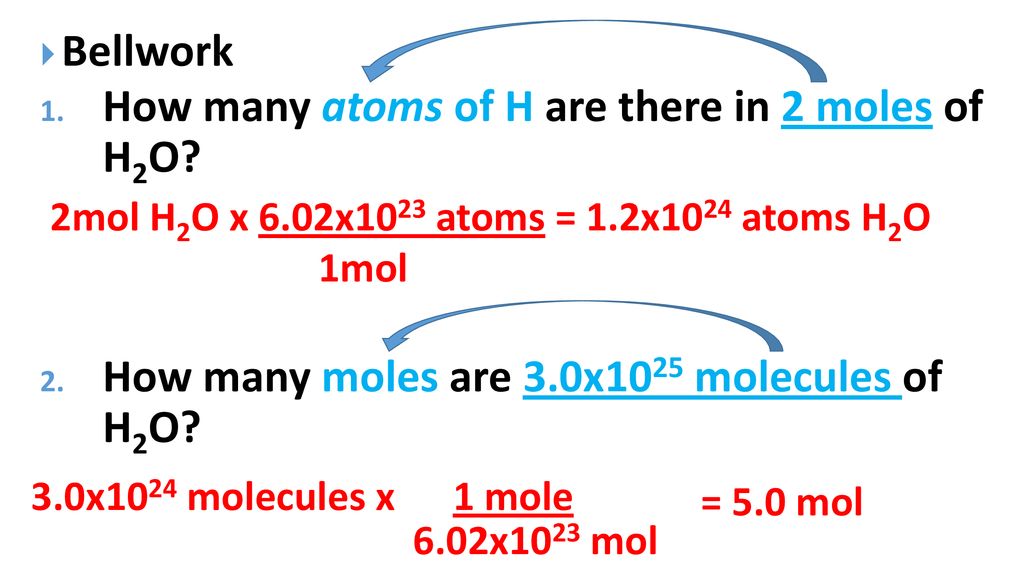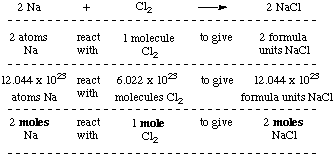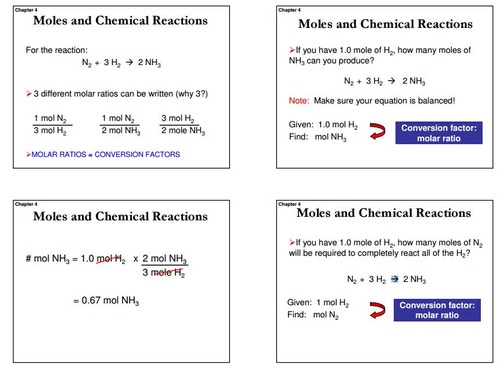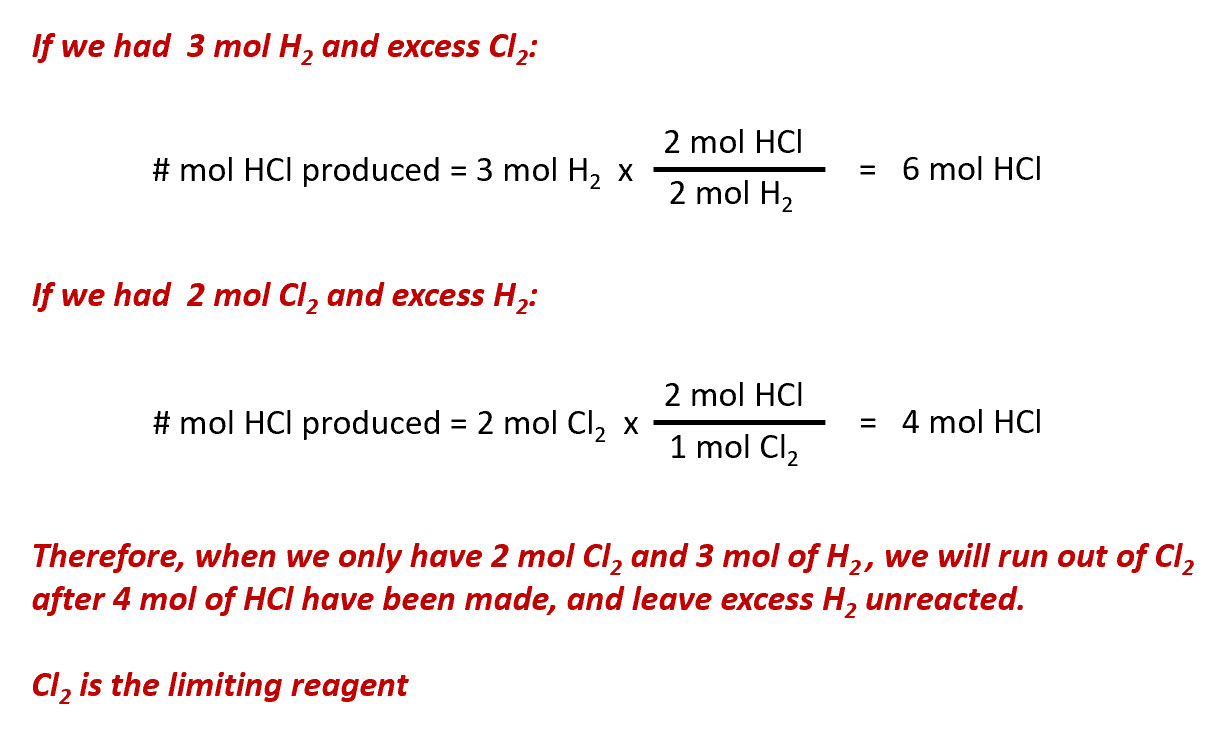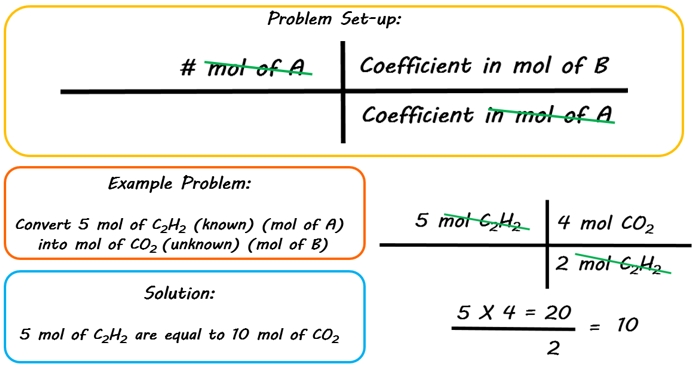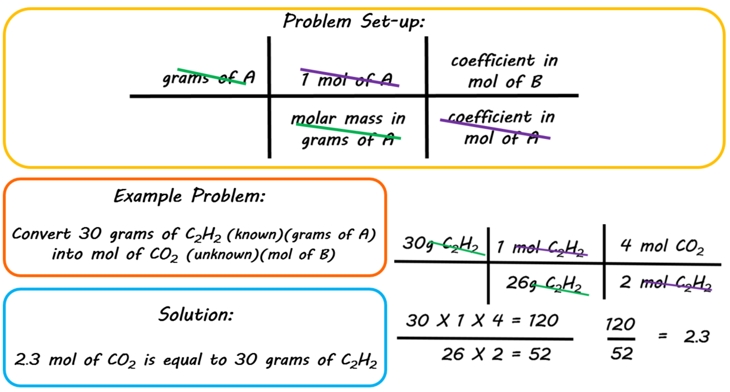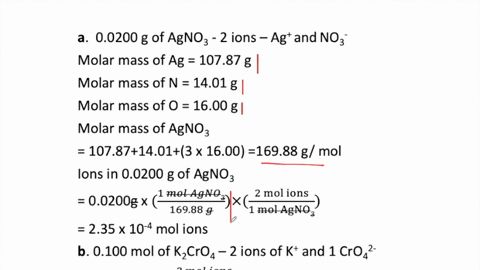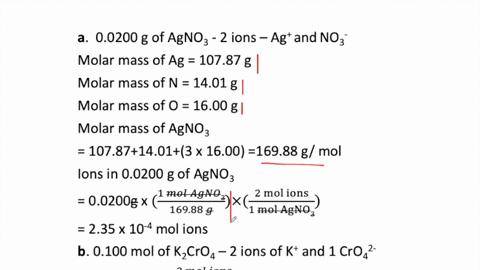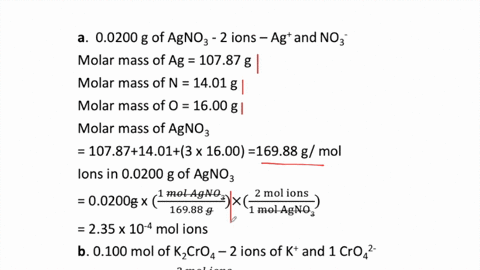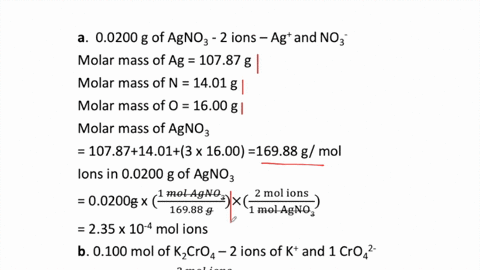
SOLVED:How many moles of ions are in each compound? a. 0.0200 g of AgNO 3 b. 0.100 mol of K2 CrO4 c. 0.500 g of Ba(OH)2 d. 1.00 ×10^-9 mol of Na2 CO3
2 mol of Hg(g) is combusted in a fixed volume bomb calorimeter with excess of O2 at 298 K - Sarthaks eConnect | Largest Online Education Community

Question Video: Identifying a Precipitating Agent for the Gravimetric Analysis of Chloride Ions | Nagwa

How to Find Moles of Product from Moles of Reactant using a Chemical Equation | Chemistry | Study.com

For a chemical reaction 2X + Y → Z, the rate of appearance of Z is 0.05 mol L^-1 min^-1 . The rate of disappearance of X will be: